Researches
My Ph.D project focuses on the atmospheres of tidally-locked rocky planets with ultra-short orbital periods.
- Atmosphere on the Close-in Rocky Planet 55 Cancri e
The ultra-short period super Earth 55 Cancri e offers a unique opportunity to study planets in extreme environment. Despite extensive observation, the nature of 55 Cancri e, however, is still poorly understood. Few model with realistic radiative transfer has been employed for hot (non-habitable) rocky exoplanets, mainly due to the incompatibility of standard GCM radiative transfer codes with currently observed hot exoplanets. Here we calculate the absorption cross section from ExoMol line lists. We develop custom correlated-k coefficients from the absorption cross section and validate them against line-by-line radiative transfer.Absorption cross section of CO2 at Earth Temperature (300 K) and typical temperature on substellar point of 55 Cnc e (3500K) assuming 1 bar pressure. The two lines are clearly distinguished. So the standard GCM radiative transfer for Earth cannot be applied to 55 cnc e.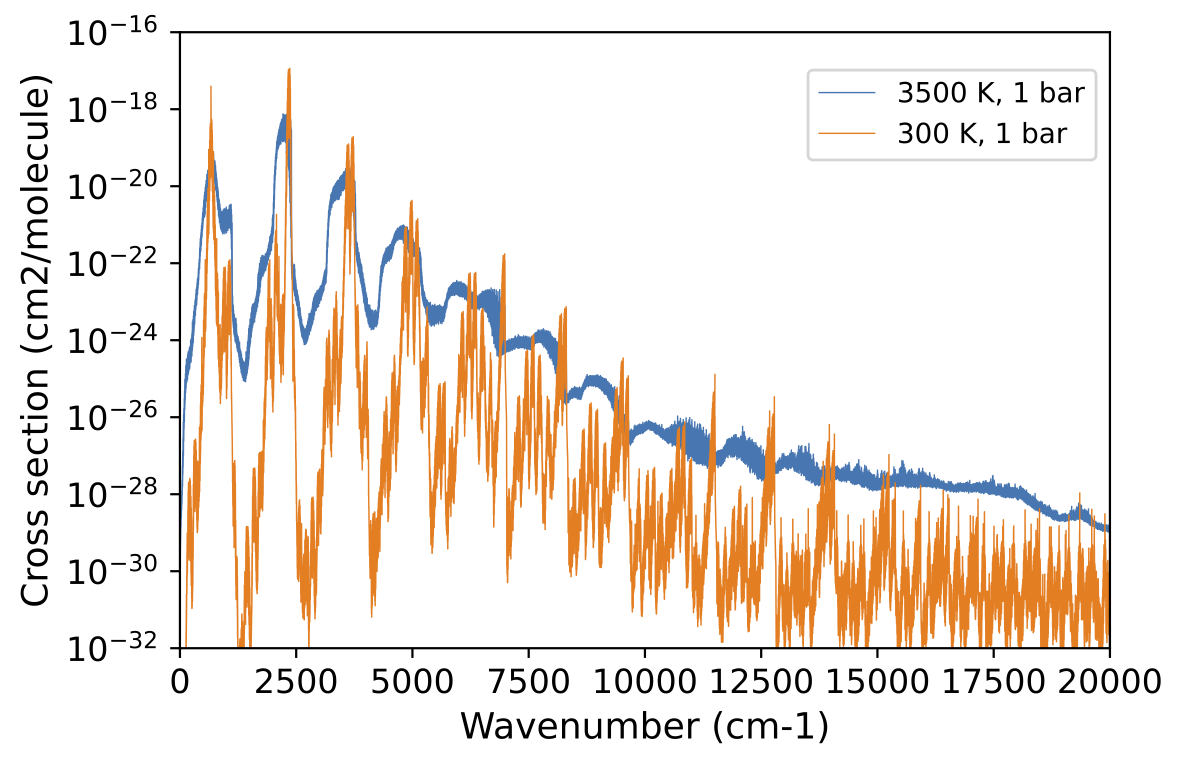
We then perform GCM simulations with non-grey radiative transfer, Isca coupled with SOCRATES, to model the atmospheres on 55 Cancri e.The gas absorption in our model includes molecular spectrum (including UV absorption) and collision induced absorption (CIA).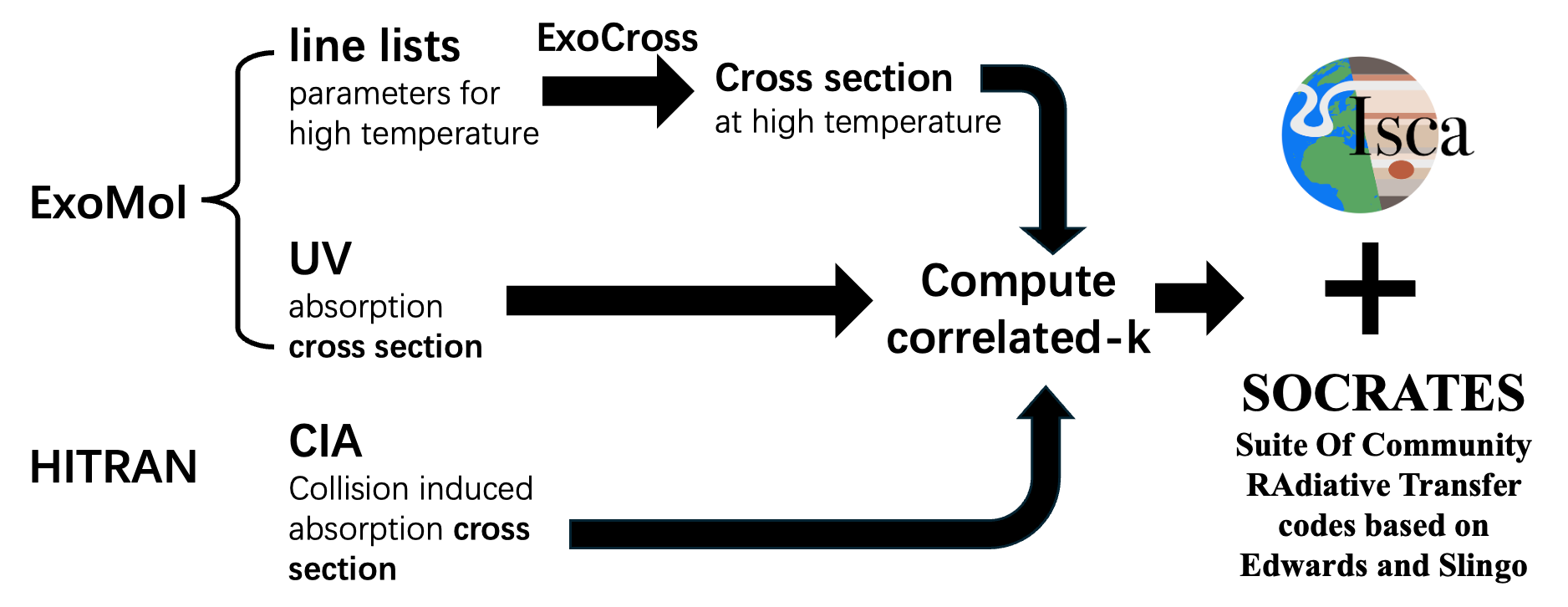
Our simulations suggest the secondary atmosphere on 55 Cancri e should be thick and carbon dioxide rich.
Observations from Spitzer and JWST reported significant time variability in the secondary eclipse depth of 55 Cancri e. However, our result suggests that clearsky atmosphere variability is much weaker than observed.
- Habitable Zone Around "Dead Stars"?
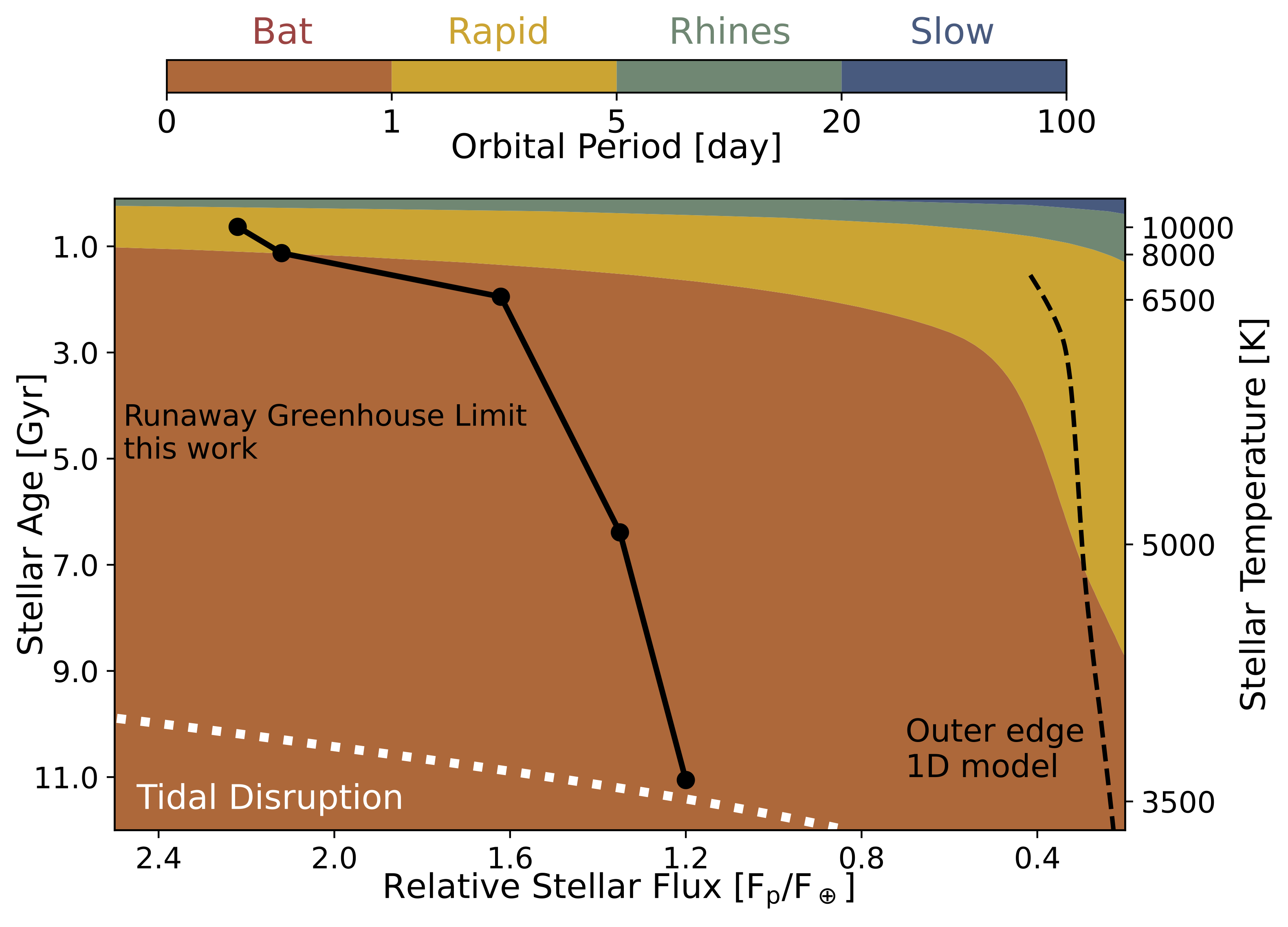
White dwarfs offer a unique opportunity to search nearby stellar systems for signs of life, but the habitable zone around these stars is still poorly understood. We use the ExoCAM Global Climate Model to investigate the inner edge of the habitable zone (HZ) around white dwarfs. Since white dwarf stars are compact and small, planets orbiting them are assumed tidally locked with ultra short orbital period (2.5hr<P<4days). Our results suggest novel atmospheric dynamics expand the inner edge of the habitable zone around white dwarfs and can be distinguished by JWST via thermal phase curve. Read more on [arxiv]/ [journal].Surface temperature and zonal mean zonal wind as a function of rotation period. From left to right: bat rotator (P = 0.5 days; this work), compared to a rapid rotator (P = 2 days), Rhines rotator (P = 10 days), and slow rotator (P = 20 days).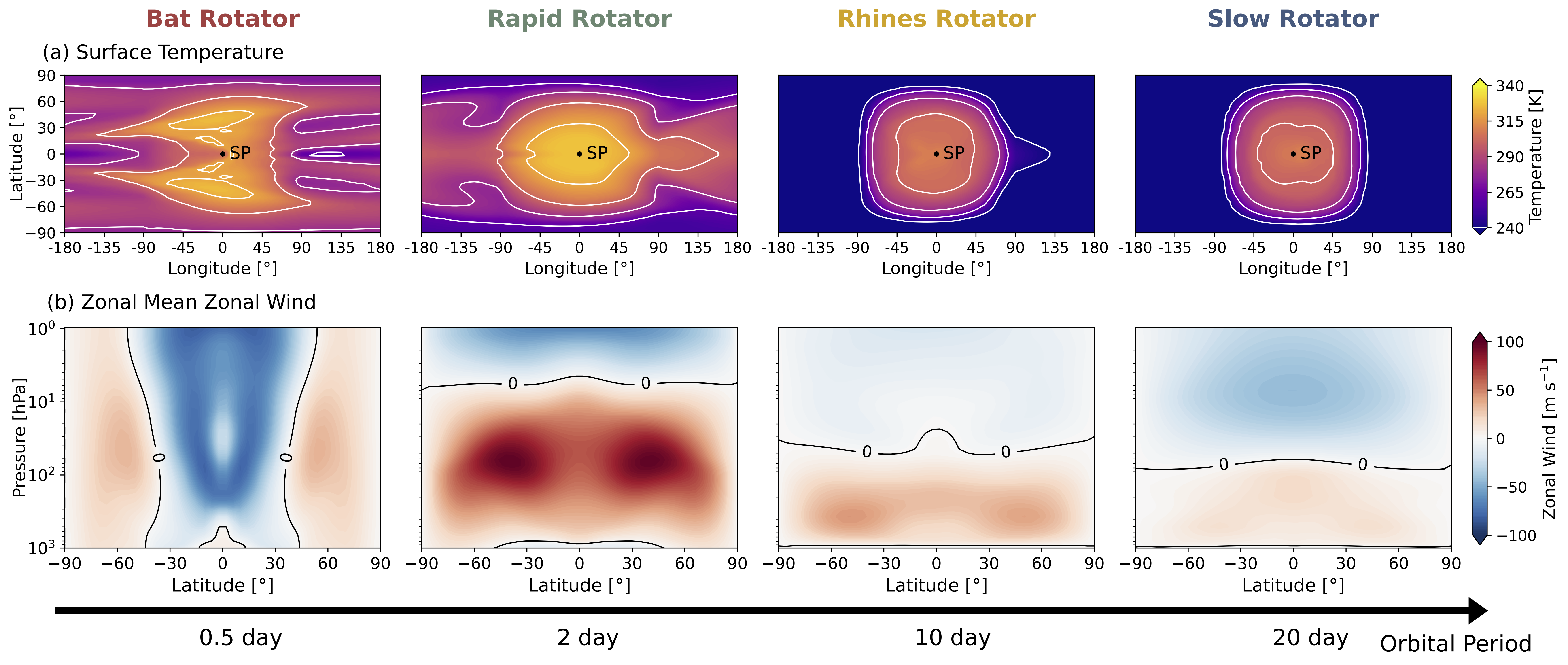 The Runaway Greenhouse Limit (RGHL) around white dwarfs, and comparison to previous studies.
The Runaway Greenhouse Limit (RGHL) around white dwarfs, and comparison to previous studies.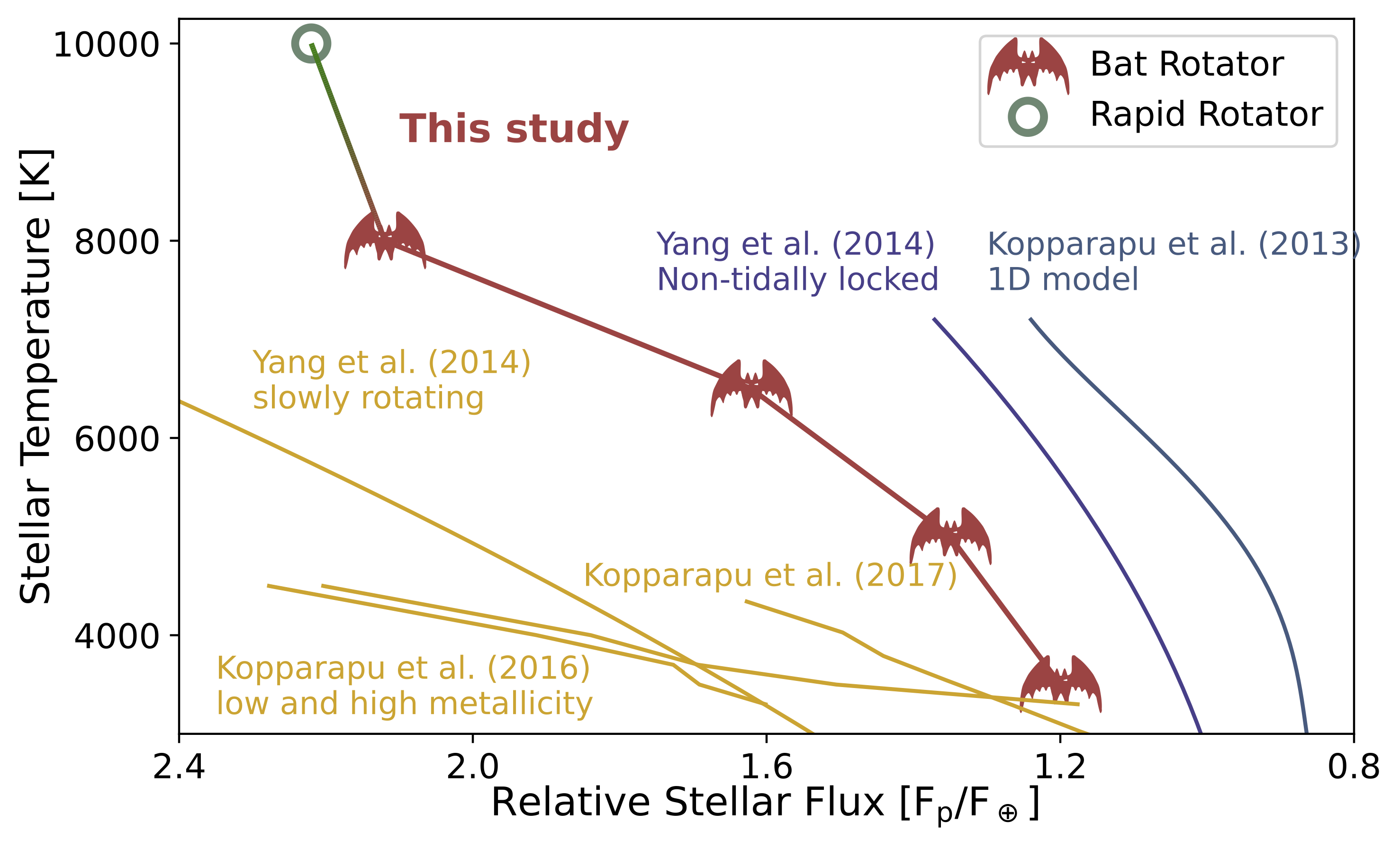 Estimated rotation regimes inside the habitable zone of white dwarfs with different stellar temperatures, as a function of relative stellar flux.
Estimated rotation regimes inside the habitable zone of white dwarfs with different stellar temperatures, as a function of relative stellar flux.